Agora
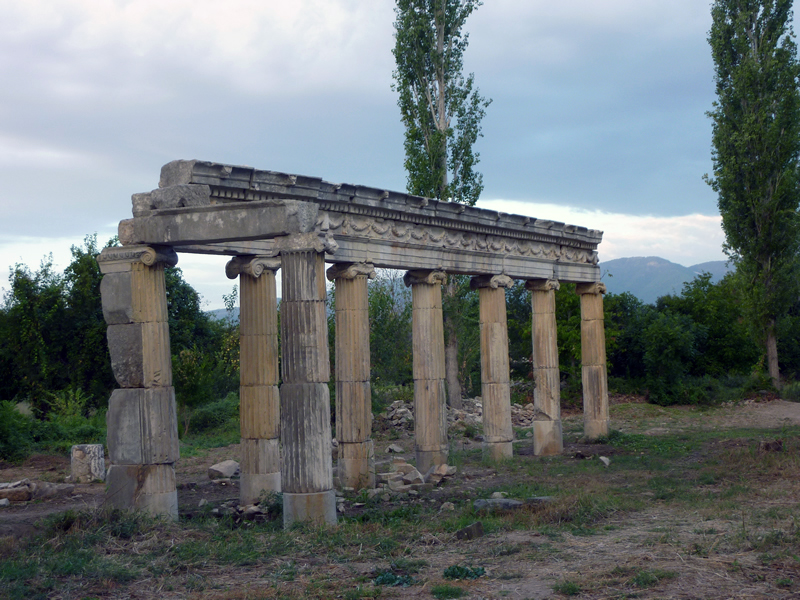
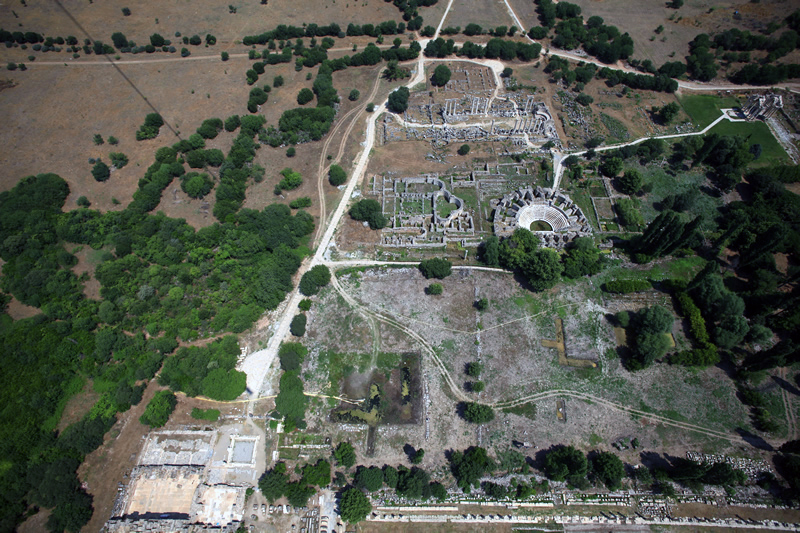
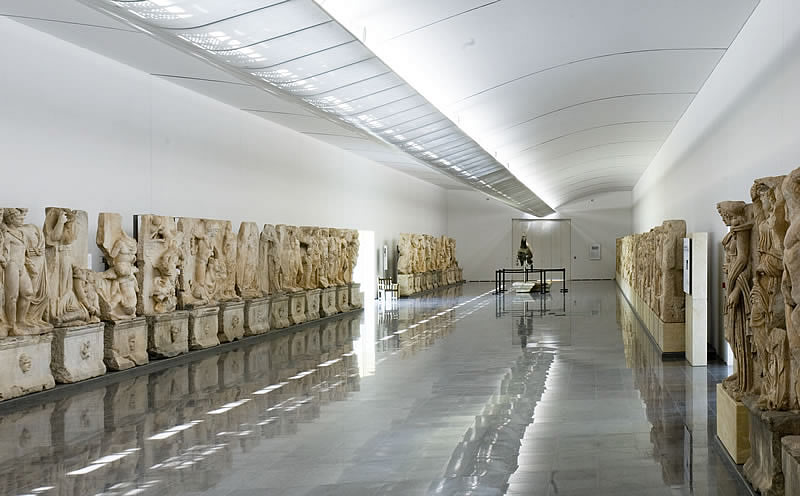
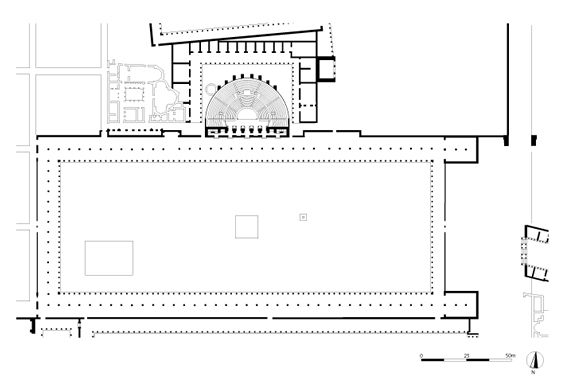
The Agora was the main civic square of the town and was one of the first components of the late hellenistic city plan to be built up in marble architectural style. It was an enclosed space (c. 202 x 72 m) surrounded by Ionic porticos on all sides. A fragmentary architrave inscription from the double north colonnade records its dedication by C. Julius Zoilos, the leading figure in the town in the 30s and 20s BC. The south colonnade of the Agora was added later, under the emperor Tiberius (AD 14-37), to whom it was dedicated. This double colonnade was built in a single unit, back to back, with the Ionic colonnade on the north side of the Urban Park. New archaeological investigation of the Agora in 1994 discovered the position and line of the west colonnade of the square and showed that the Agora was laid out with the Council House on its central axis.
Finds: Oecumenius






